大数据学习笔记2-Hive、Hbase

Hadoop2
七.Hive
- 不统计是不走mapReduce的
- 最后ADS中的内容就是要被调用而不被调用的
- 默认走MapReduce引擎
(一)前期
什么是
- 基于Hadoop的数据仓库解决方案
- 将结构化的数据文件映射为数据库表
- 提供类sql的查询语言HQL(Hive Query Language)
- Hive让更多的人使用Hadoop
优势和特点
提供了一个简单的优化模型
HQL类SQL语法,简化MR开发
支持在不同的计算框架上运行
支持在HDFS和HBase上临时查询数据
支持用户自定义函数、格式
常用于ETL操作和BI
ETL:加载清理转化
BI:做图表
稳定可靠(真实生产环境)的批处理
有庞大活跃的社区
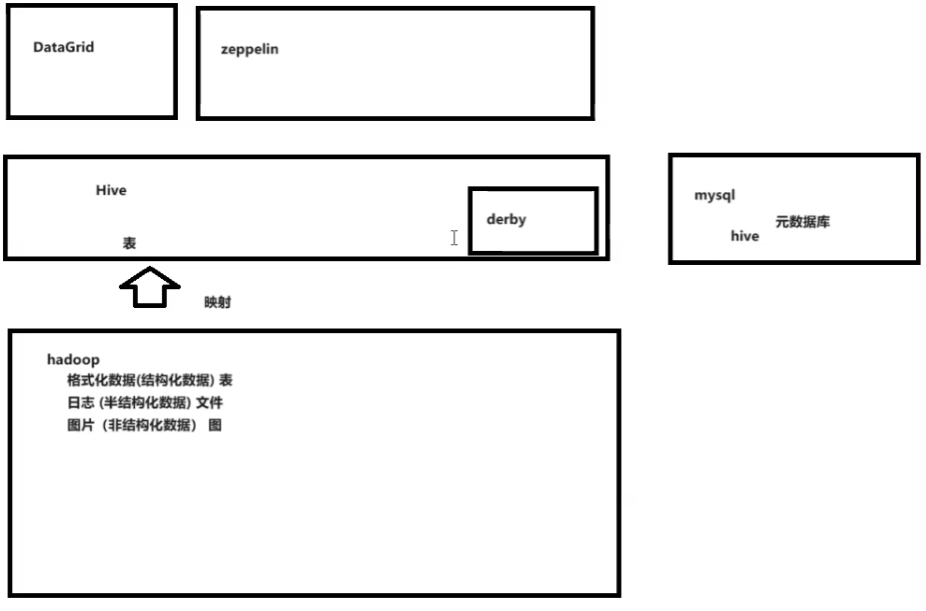
工作原理
映射hadoop数据成表
本身不存数据
自带一个小型数据库derby(相当于元数据库),但是还是太小,再架设一个mysql为hive数据库。
图例和解释
Hive把hadoop元数据映射到mysql,用zeppelin来当数据库控制工具。
Hive相当于是一个中转的数据仓库,mysql中存元数据,hdfs中存原始数据,外部调用hive来结构化的查询。

做个人数据表映射的时候,脱敏操作,即敏感数据可以不映射
(二)内容
- 数据库中大部分和Mysql一样,但是没有约束和主外键
(三)hive安装配置
安装好hadoop
安装好mysql数据库,版本要对好,下面提前改好
1
2# vim /etc/my.cnf
character-set-server=latin1安装hive,把hive-1.1.0-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz放入/opt
解压移动编辑配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15cd /opt
tar -zxf hive-1.1.0-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz
mv hive-1.1.0-cdh5.14.2 soft/hive110
vim /etc/profile
填入
#Hive Env
export HIVE_HOME=/opt/soft/hive110
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin
# 保存退出
source /etc/profile
cd /opt/soft/hive110/conf
vim hive-site.xmlvim hive-site.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46填入
# 第一个目录是自己改的
# 第二个true为本地,false为其他IP
# 下面的ip要相应改
# 最下面密码别忘了
<configuration>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.warehouse.dir</name>
<value>/hive/warehouse</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.local</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL</name>
<value>jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName</name>
<value>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword</name>
<value>ok</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.authentication</name>
<value>NONE</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.user</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hive.server2.thrift.client.password</name>
<value>root</value>
</property>
</configuration>上传一个mysql驱动包到hive110下的lib
驱动包是mysql-connector-java-5.1.38.jar,在maven下面的库中
jps确保五个服务都是启动状态,没有的话stop-all.sh;start-all.sh
启动hive服务(只能黑界面)
1
hive --service metastore
启动后独占窗口,不能关闭
jps多了RunJar
后台启动:
nohup hive --service metastore &两下回车,但没有返回值再开一个新窗口,启动hive远程服务
1
hive --service hiveserver2
启动后独占窗口,不能关闭
jps多了RunJar
后台启动:
nohup hive --service hiveserver2 &但没有返回值要使用再开窗口
hive命令直接进入数据库
创建数据表的时候可能会错,
MySQLSyntaxErrorException: Column length too big for column 'PARAM_VALUE'退出后进入mysql -uroot -pok
1
2
3alter database hive character set latin1;
flush privileges;
show variables like 'char%'; -- 这句可以查看编码
解释
要是会有扫描数据找不到
就执行初始化
schematool -dbType mysql -initSchema数据库元数据初始化命令:
schematool -dbType derby -initSchema
(四)zeppelin安装配置
- zeppelin时远程使用hive映射数据库的
zeppelin-0.8.1-bin-all.tgz放到/opt下
解压
1
2
3
4
5
6cd /opt
tar -zxf zeppelin-0.8.1-bin-all.tgz;
mv zeppelin-0.8.1-bin-all soft/zeppelin081;
cd soft/zeppelin081/conf/;
cp zeppelin-site.xml.template zeppelin-site.xml
cp zeppelin-env.sh.template zeppelin-env.shvim zeppelin-site.xml,加一个
1
2
3
4<property>
<name>zeppelin.helium.registry</name>
<value>helium</value>
</property>vim zeppelin-env.sh
这里面还能改内存、核
1
2export JAVA_HOME=/opt/soft/jdk180
export HADOOP_CONF_DIR=/opt/soft/hadoop260/etc/hadoop1
2
3cp /opt/soft/hive110/conf/hive-site.xml /opt/soft/zeppelin081/conf/
cp /opt/soft/hadoop260/share/hadoop/common/hadoop-common-2.6.0-cdh5.14.2.jar /opt/soft/zeppelin081/interpreter/jdbc/
cp /opt/soft/hive110/lib/hive-jdbc-1.1.0-cdh5.14.2-standalone.jar /opt/soft/zeppelin081/interpreter/jdbc/上传包java-json.jar
把这个包放到
/opt/soft/zeppelin081/lib中配置环境变量
vim /etc/profile加入
1
2
3#Zepplin Env
export ZEPPELIN_HOME=/opt/soft/zeppelin081
export PATH=$PATH:$ZEPPELIN_HOME/binsource /etc/profile
结束
启动方法
zeppelin-daemon.sh start,在这之前要重启hive
(五)使用
1.第一次使用
- 黑界面直接hive进入数据库
- 创建
1 | create database mydemo; |
创建数据表的时候可能会错,
MySQLSyntaxErrorException: Column length too big for column 'PARAM_VALUE'- 退出后进入mysql -uroot -pok
1
2alter database hive character set latin1;
flush privileges;
插入数据
1
insert into userinfos values(1,'zs','1999-10-12'),(2,'ls','2000-10-12');
- 速度很慢,因为用了mapreduce的mapper
读数据
1
select * from userinfos;
- 速度很快,没有mapreduce
- 但是用聚合或者统计就会使用mapreduce,速度特别慢
在hdfs下/hive/warehouse/mydemo/userinfos下有相应数据
这个路径是配置hive的时候自己的路径
2.远程连接和使用
第三方软件连接测试
远程执行命令要开着
1
hive --service hiveserver2
在命令行下beeline
是自己改的hive配置的密码,再输入密码
1
!connect jdbc:hive2://192.168.179.139:10000
退出时
!qzeppelin安装好
启动zeppelin,在这之前要启动hive
1
zeppelin-daemon.sh start
远程连接
浏览器访问http://ip:8080/
使用下面是
界面右上角anonymous->Interpreter
create一个新的集成环境叫hive,用的是jdbc
在配置中配置
1
2
3default.driver org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver
default.url jdbc:hive2://192.168.42.200:10000
default.user root相应位置要输入密码
点击保存
点击上面的Noteboook->create new note
notename随便这边firsthive
默认的数据仓库(不是数据库)选hive
进入后就可以用sql语句了
但是这边不能使用
;,每一句只能单行,如果要查某个数据库中的数据,就要如下select * from mydemo.userinfos除此之外
用%sh还可以指定使用的解释器
3.DataGrip远程连接
- 开启hadoop和hive
1 | start-all.sh |
- 配置datagriphive数据库
- 记得改驱动可以在hive下的lib找形如
hive-jdbc-1.1.0-cdh5.14.2-standalone.jar要对应相应的版本
(六)详细学习
- 函数没转过去会出空
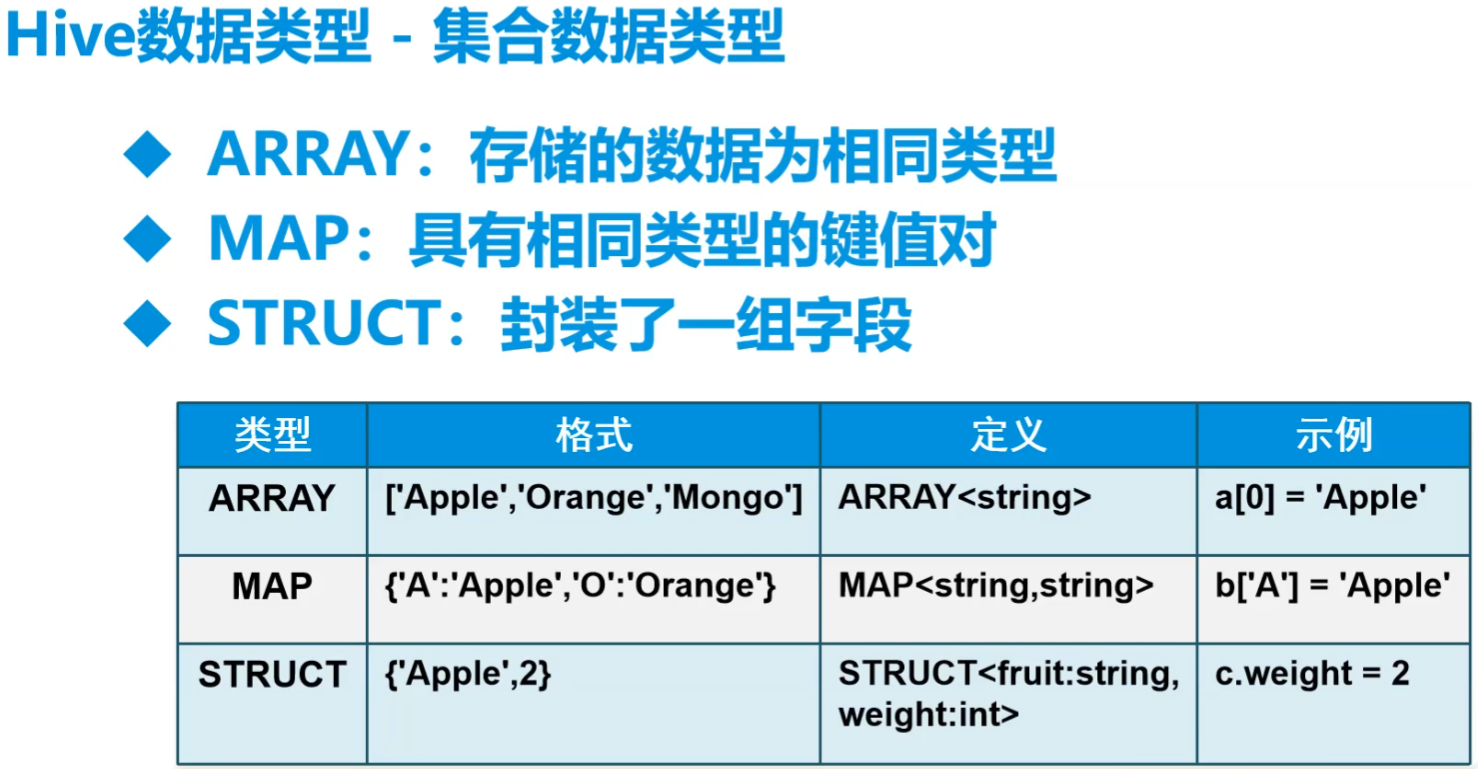
1.数据类型
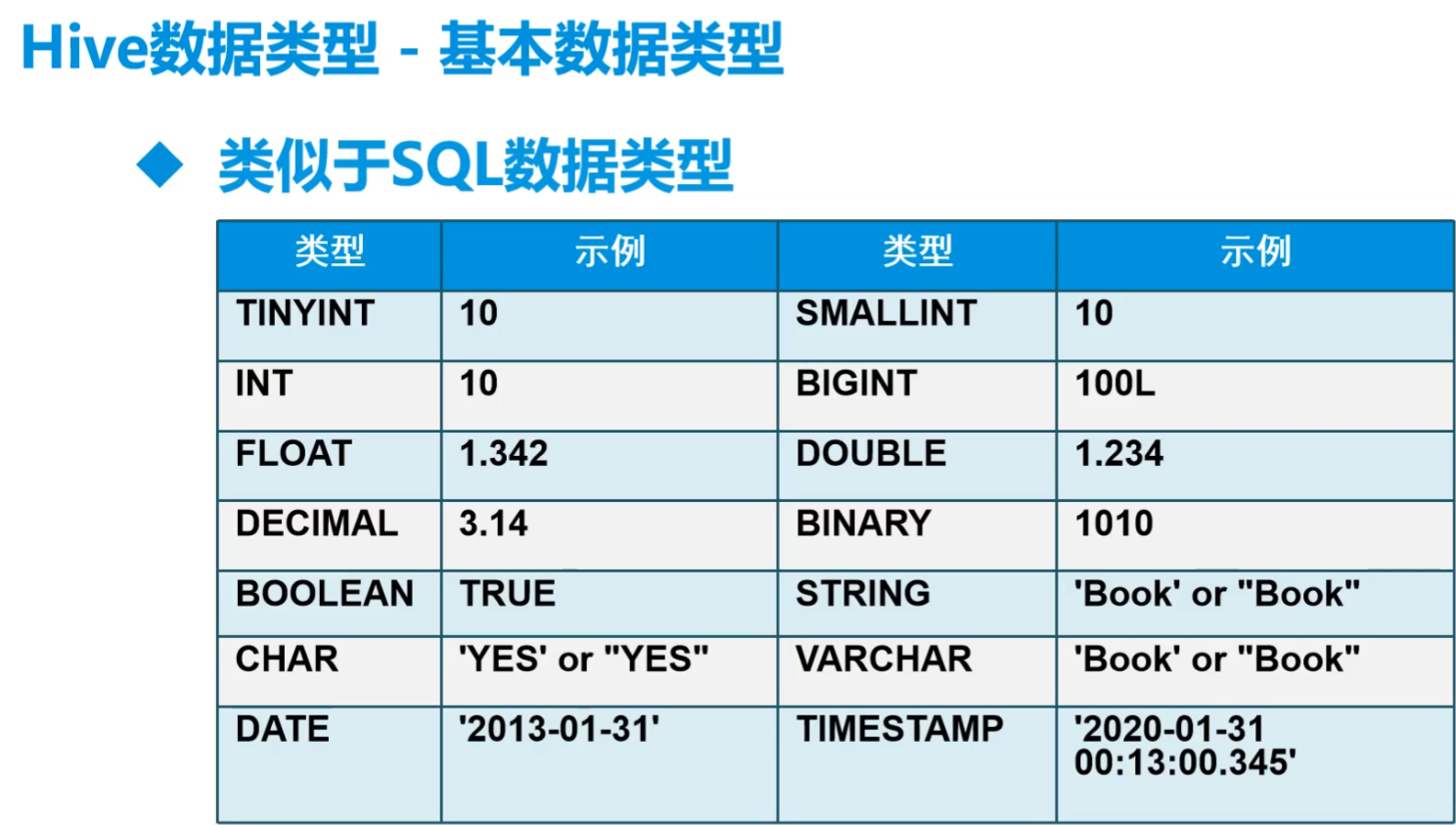
string类型用的最多,数仓尽量用string
数据清洗就要转化为其他类型
比mysql中多了复杂类型数据

- struct相当于一个对象
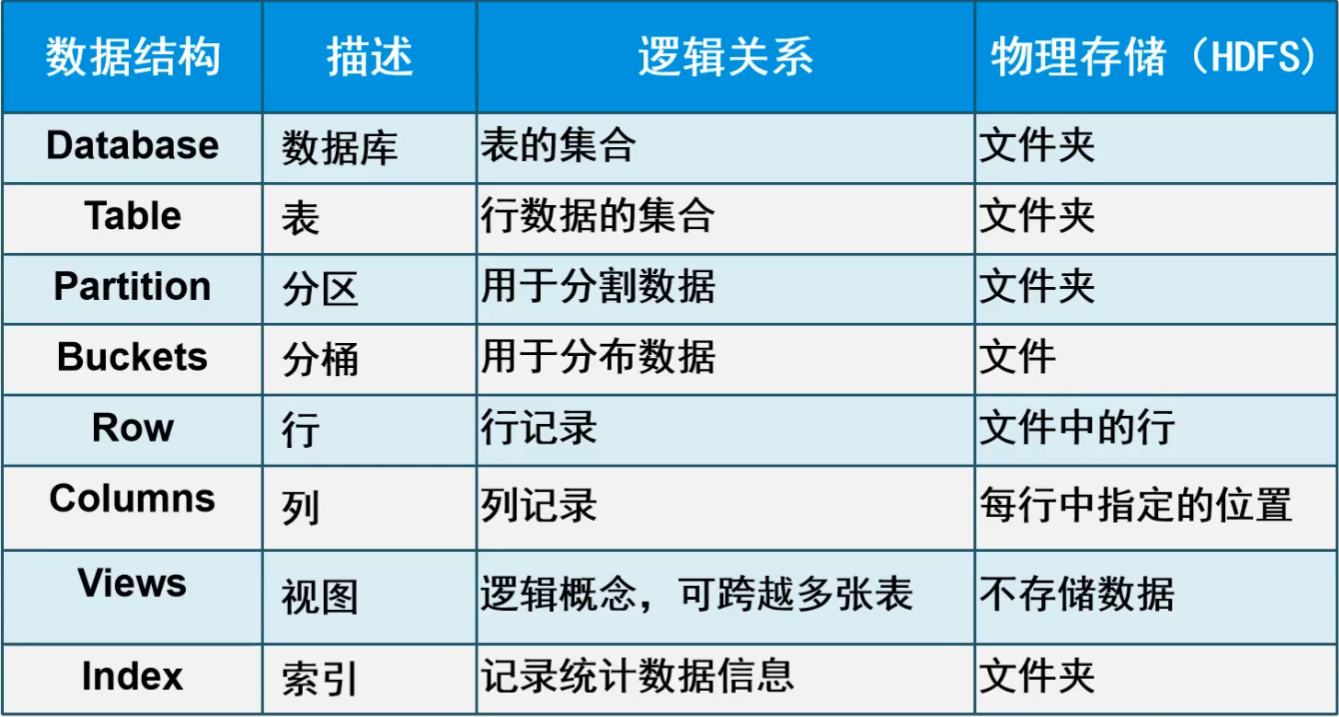
2.Hive数据结构

- partition分区为了方便找数据
- buckets在抽样过程中
3.数据库操作

- cascade是关联删除,会把依赖于主键的全删了
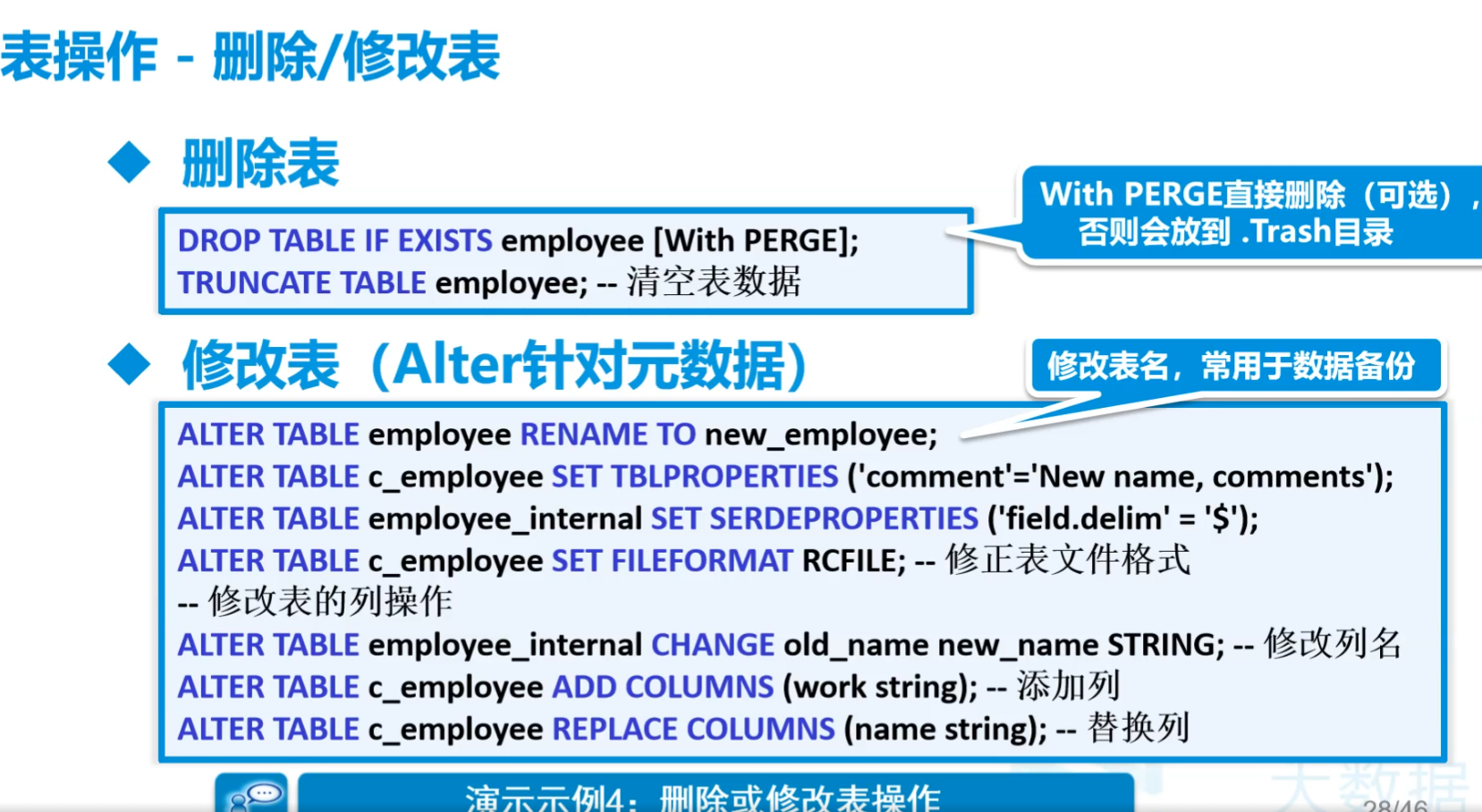
4.表操作

默认的分隔符是SOH即为
\001regexp_replace相当于replace
还有temporary临时表,会话结束就没了
nvl()判断第一个表达式是否为null,
nvl(判断,否的话执行这条)insert into追加
insert overwrite覆盖

用这种方式就默认都是SOH
创建内部表
十分危险,删除表会连带着hdfs内部的数据全部删除,而非只删除元数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12--创建一个内部表
create table if not exists student(
id int, name string
)
-- 设置分隔符,默认SOH
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
-- 设置存储格式 除了textfile,ORC和Parquet是两个广泛使用的
stored as textfile
-- 设置存储位置 这个是可以自己定义的
location'/home/hadoop/hive/warehouse/student'
--查询表的类型
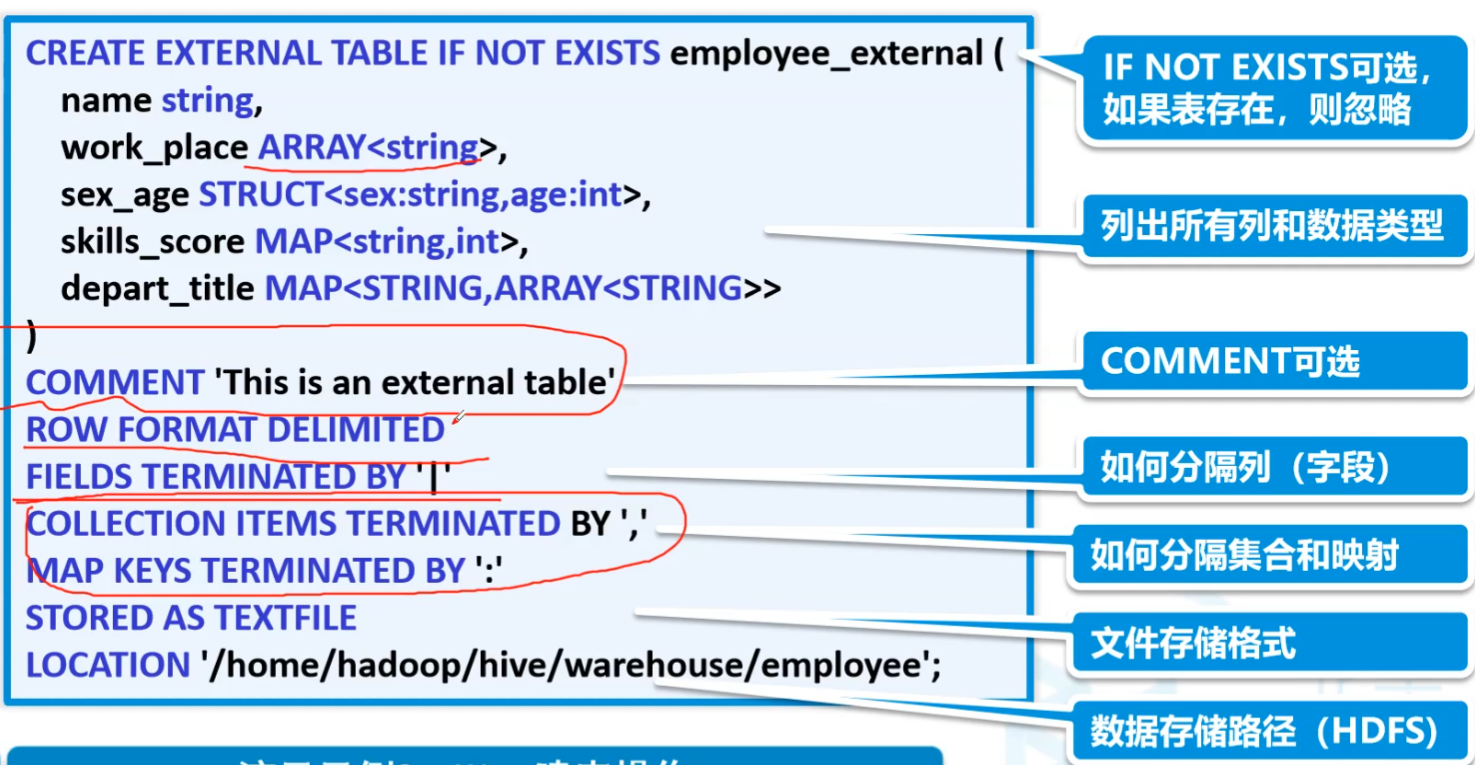
desc formatted student;创建外部表
只删元数据,不删数据本体
1
2
3create external table if not exists student(
id int, name string
)复杂类型分割
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
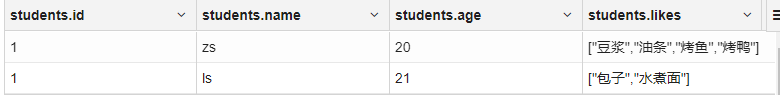
10create external table mydemo.students(
id int,
name string,
age int,
likes array<string>
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':'
tblproperties("skip.header.line.count"="1") -- 跳过多少行
location '/towers/students'1
21,zs,20,豆浆:油条:烤鱼:烤鸭
1,ls,21,包子:水煮面结果

数据采集
就是数据放到hdfs,创建外部表做映射
高阶建表语句
这样建立的表是内部表
而且底层数据复制了一份放在了默认的路径中
1
create table mydemo.friends1 as select * from mydemo.friends
用途:新建底层数据,在上面的select语句中加上where等,用于过滤数据。实际上数据仓库中就建立多层数据,映射、加工、服务一层一层的来过滤数据,需要很多中间表,就是上的的方法。
还可以这样子,就不会有数据 like
1
create table mydemo.friends2 like mydemo.friends
创建临时表
删除表
- 删掉整个
1
truncate table mydemo.friends
不能用delete,因为照道理原始数据是不能改的

数据表分割问题
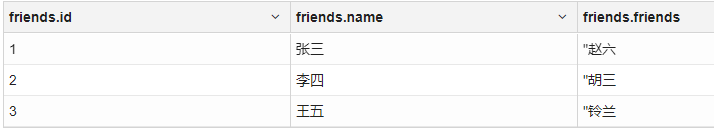
朋友表,用excel出来的元数据如
1
2
31,张三,"赵六,宋七"
2,李四,"胡三,李儒"
3,王五,"铃兰,张无忌,赵敏"用下面的语句会出错
1
2
3
4
5
6
7create external table mydemo.friends(
id int,
name string,
friends string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
location '/towers/friends'
这时候就有一个东西叫做:解析器
5.解析器serde
先解决4中的最后一个问题
如下就没问题了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14%hive
create external table mydemo.friends(
id int,
name string,
friends string
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
with serdeproperties(
"separatorChar"=",",
"quoteChar"="\"",
"escapeChar"="\\"
)
-- row format delimited fields terminated by ','
location '/towers/friends'
"separatorChar"=",":这个属性指定了字段之间的分隔符。在这个例子中,分隔符被设置为逗号(,),这是CSV文件中最常见的分隔符。"quoteChar"="\"":这个属性指定了用于包围字段值的字符,当字段值中包含分隔符、引号字符或换行符时,通常会用这些引号字符将字段值包围起来。在这个例子中,引号字符被设置为双引号(")。"escapeChar"="\\":这个属性指定了用于转义引号字符内的特殊字符的转义字符。然而,在CSV的上下文中,这个属性的具体行为可能会因实现而异,因为CSV标准本身并没有明确定义转义字符的使用。在OpenCSVSerde中,这个属性可能用于处理引号字符内部的引号字符(例如,通过前置一个反斜杠来转义引号),但这取决于OpenCSVSerde的具体实现和配置。然而,需要注意的是,在提供的例子中,转义字符被设置为反斜杠(\),但字符串值中的反斜杠自身需要被转义(即写成\\),这在许多编程语言中都是必要的,以确保反斜杠被正确地解析为字符串中的一个字符,而不是作为转义字符的开始。
6.内部结构
直接把相应格式的文件放到dfs中的相应目录中,就可以直接读取
因此可以在命令终端直接put
7.数据表上锁
当做删除等操作的时候一直运行没响应
把字符集改为latin1
1
2
3
4# vim /etc/my.cnf
character-set-server=latin1
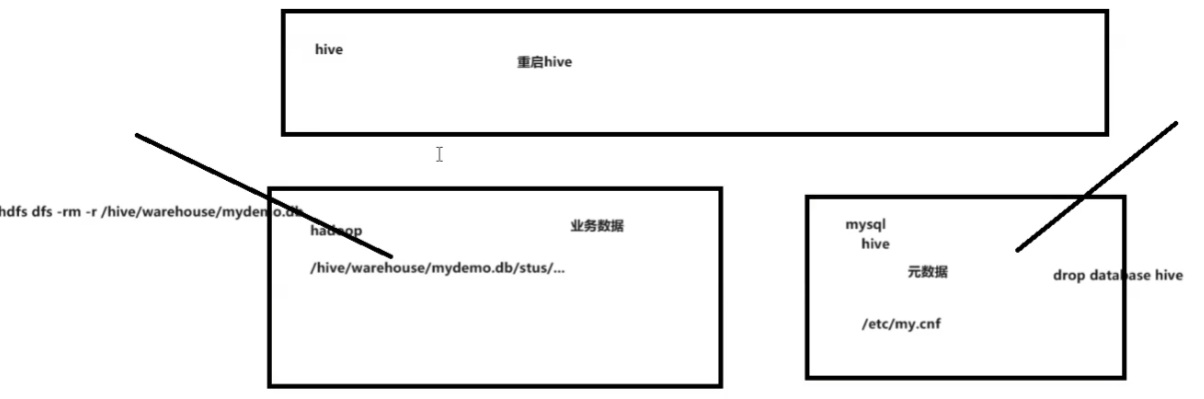
重启服务service mysqld restart关闭zeppelin和hive
重启hive

8.装载数据LOAD
也可以在hdfs dfs -put来导入
LOAD用于在Hive中移动数据

- LOCAL:指定文件位于本地文件系统,执行后为拷贝数据
- OVERWRITE:表示覆盖表中现有数据
示例
把linux上的数据文件加载到mydemo.students的数据表
如果没有overwrite,就相当于是追加
1
2
3
4%hive
load data local inpath '/opt/testdata/t.txt'
overwrite into table mydemo.students
-- select * from mydemo.students
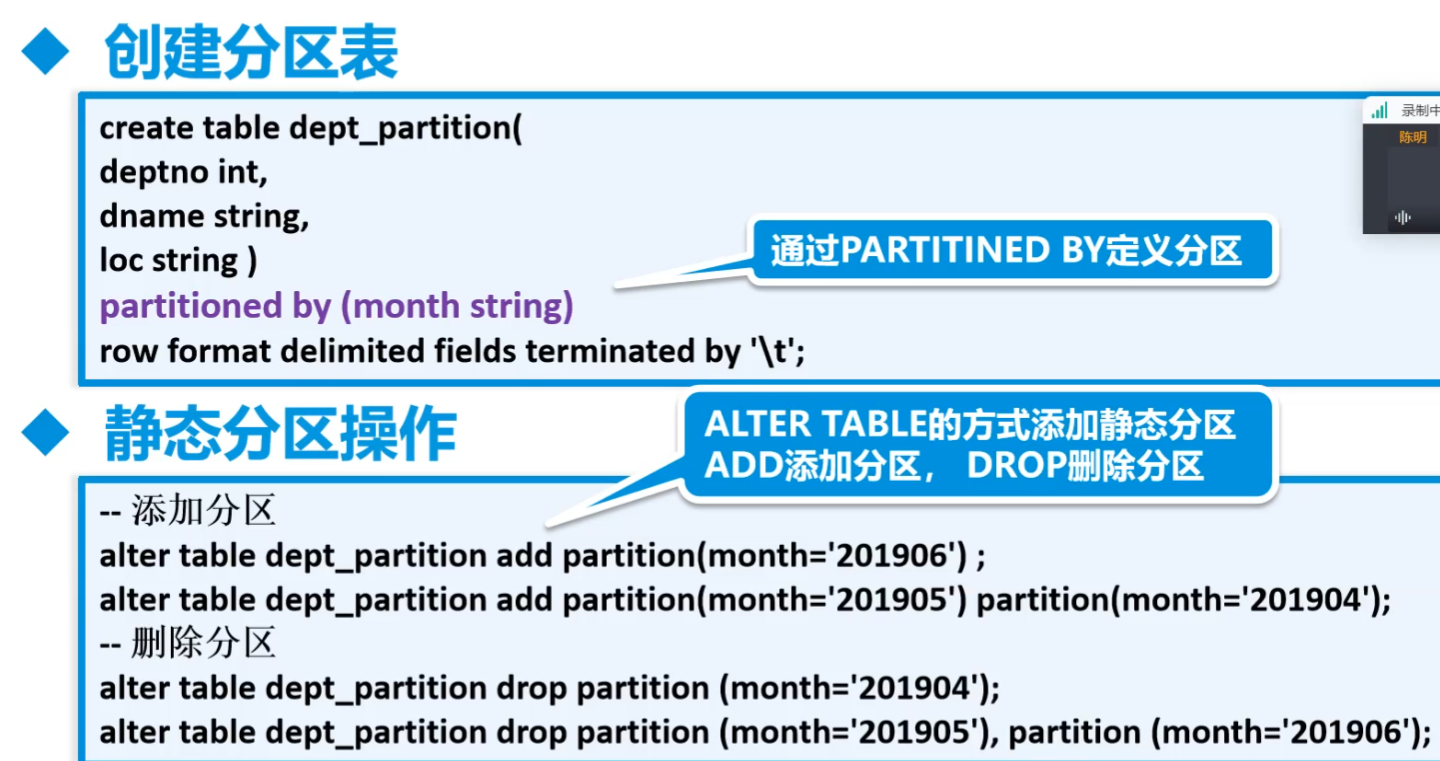
9.Hive分区(Partition)
A.介绍
分区主要用于提高性能
- 分区列的值将表划分为一个个的文件夹
- 查询时语法使用”分区”列和常规列类似
- 查询时Hive会只从指定分区查询数据,提高查询效率
分为静态分区和动态分区
- 两者的建表过程是相同的
- 静态分区:先添加分区(建立文件夹),用户传递
- 动态分区:更具数据来判断,只有sql执行时才会确定。动态分区个数也是可调的,一般是100个。很多时候扛不住,还是要静态分区,增量计算分区,每天一点往里塞
比如销售的订单到部分按季度查,就按季度。决定粒度,取决于查询结果
分区表一般都是内部表
静态分区

动态分区
先塞数据进去,然后自动分区

B.静态例子1
吊塔运行记录每天的数据
按天来进行最小粒度的划分
先进行数据的仿真模拟
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43public class MyTowerLog {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 799 10*60*60
Random rand = new Random();
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.set(2024,0,1,8,0,0);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd");
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
// 准备五年间加名字20240101
String dirName = sdf.format(cal.getTime());
// 生成800个塔吊文件 塔吊编号+日期 zt0001_20240101.log
for(int i=0;i<=8;i++){
String path = "e:/Temp/towerdata/curr/" + dirName;
File file = new File(path);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdir();
}
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile(path + "/" + towerLogFileName(i)
+ "_" + dirName + ".log", "rw");
for(int time=0;time <10*60*60;time++){
// 时间向前加
cal.add(Calendar.SECOND, 1);
// 写日志字符串 日期时间中间加个T
String logStr = towerLogFileName(i) + " "
+ sdf1.format(cal.getTime()).replaceAll(" ", "T") + " "
+ rand.nextInt(12) + " "
+ rand.nextInt(10) + " "
+ rand.nextInt(15) + " "
+ rand.nextInt(5) + "\n";
raf.write(logStr.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
raf.write("hehe".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
raf.close();
}
}
private static String towerLogFileName(int no) {
String filename = "zk" + String.format("%04d", no);
return filename;
}
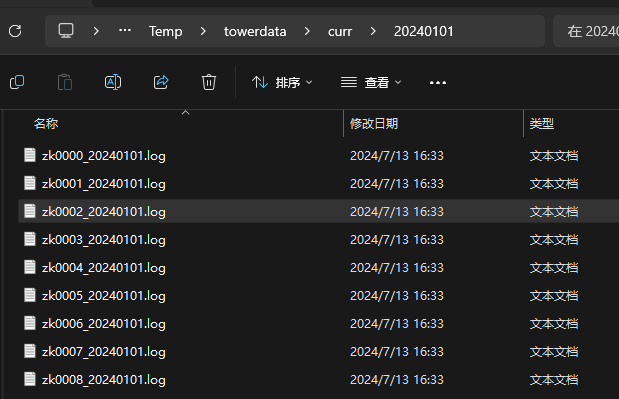
}数据文件夹如下

数据形如
1
2
3
4zk0000 2024-01-01T08:00:01 6 1 5 4
zk0000 2024-01-01T08:00:02 3 8 2 2
zk0000 2024-01-01T08:00:03 5 0 1 4
zk0000 2024-01-01T08:00:04 3 3 2 2创建分区表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11%hive
create external table mydemo.towerdatas(
id string,
ts string,
weight string,
speed string,
range string,
angle string
)
partitioned by (ymd string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ' '创建静态分区
1
2%hive
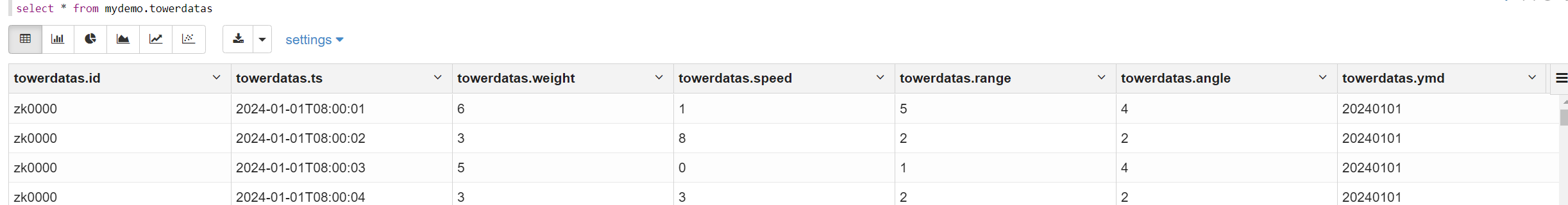
alter table mydemo.towerdatas add partition(ymd='20240101')载入数据
1
2%hive
load data local inpath '/opt/testdata/20240101/' into table mydemo.towerdatas partition(ymd='20240101')最终结果

实际中要用脚本每天把数据放入
hive -e "命令"可以直接运行,当然也可以echo "命令" | hive这样来运行远程脚本可以如下,这个脚本要在能够ssh免密登录的时候才可以这样做
实际要做的步骤
- 将日志服务器上的数据传递给hadoop集群
- 在hive上的某个分区表上添加分区
- 将本地接到的数据加载到这个分区中
- 删除本地数据
- 每天都要做(crontab定时任务)
脚本示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16# 获取当天日期,按照实际要是前一天,而不是当天的
foldername=`date +"%Y%m%d"`
scp -r /opt/data/$foldername root@192.168.179.139:/opt/towerdata/
# 在hive的towerdatas表中建立昨日分区
CREATEPARTITIONSTR="alter table mydemo.towerdatas add partition(ymd='${foldername}');"
echo "hive -e \"$CREATEPARTITIONSTR\"" | ssh root@192.168.179.139
# 将本地数据导入昨日分区
IMORTDATASTR="load data local inpath '/opt/towerdata/$foldername' into table mydemo.towerdatas partition(ymd='$foldername')"
echo "hive -e \"$IMORTDATASTR\"" | ssh root@192.168.179.139
# 将linux上的数据删除
echo "rm -rf /opt/towerdata/$foldername/" | ssh root@192.168.179.139
# 删除半年前的数据分区
foldername=`date -d "-196 day" '+%Y%m%d'`
DROPPARTITIONSTR="alter table mydemo.towerdatas drop partition(ymd=$foldername)"
echo "hive -e \"$DROPPARTITIONSTR\"" | ssh root@192.168.179.139crontab设置定时任务
crontab -e1
2
3# example.cron
1 * * * * source ~/example.sh
# 每一分钟执行一次
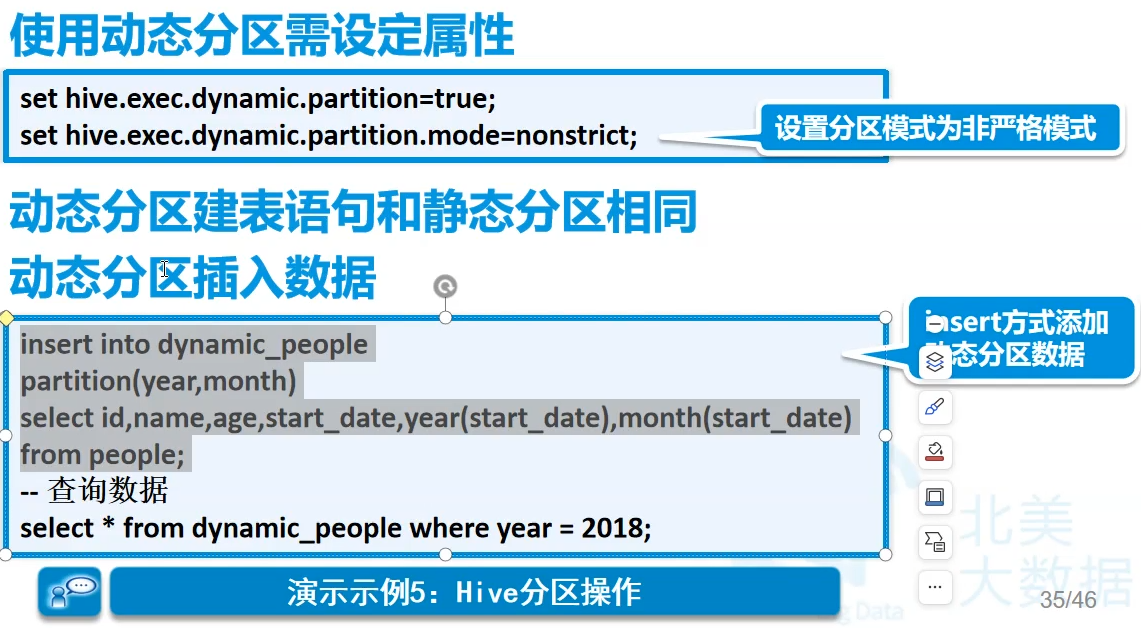
C.动态例子1
过程
- 将一堆数据导入hdfs
- 在hadoop上使用归档把所有数据压缩到一个文件中
- 在hive建立一个临时的表并存储数据
- 将临时表的数据通过insert语句动态存放到分区表中
数据仿真
很多很多天的数据以单条目生成,小改了一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7//生成300天数据
for(int day=0;day<300;day++) {
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.set(2024, 0, 1, 8, 0, 0);
cal.add(Calendar.DATE, day);
// 准备五年间加名字20240101
String dirName = sdf.format(cal.getTime());过程
在hadoop建立一个临时文件夹并上传所有数据到临时文件夹
1
2
3hdfs dfs -mkdir /datatmp
hdfs dfs -put /opt/towerdata /datatmp
hdfs dfs -mkdir /dataarchive # 执行一次就够了由于小文件过多所以使用hadoop将众多的小文件进行归档
hadoop archive -archiveName data1.har -p /datatmp/towerdata /dataarchive查看归档文件信息
1
hdfs dfs -cat /dataarchive/data1.har/part-0
在数据仓库中创建一个临时表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10create temporary table mydemo.temps(
id string,
ts string,
weight string,
speed string,
range string,
angle string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ' '
location '/dataarchive/data1.har'将临时表的数据使用insert语句导入到分区表中
导入过程不一定吃得消,要么就脚本分段导入要么调整hadoop参数,网上找好,包括线程数,内存数
1
2
3
4
5
6hdfs-site.xml中
<property>
<!--datanode上负责进行文件操作的线程数-->
<name>dfs.datanode.max.transfer.threads</name>
<value>32768</value> 改大小默认4096
</property>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9-- 开启动态分区
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true;
set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;
insert into mydemo.towerdatas partition(ymd) select t.*,regexp_replace(substring(t.ts,0,10),'-','') ymd from mydemo.temps t
改为,
insert into mydemo.towerdatas partition(ymd)
select * from (select t.*,regexp_replace(substring(t.ts,0,10),'-','') ymd from mydemo.temps t) f where f.ymd like '2024012%'
要性能调优- 写快出问题了,调整文件句柄数,提高线程数,同时不让超过内存
10.分桶
A.知识点
Bucket
分桶对应于HDFS中的文件
- 更高的查询处理效率
- 使抽样(sampling)更高效
- 一般根据”桶列”的哈希函数将数据进行分桶
分桶只有动态分桶
1
SET hive.enforce.bucketing = true;
定义分桶
1
CLUSTERED BY (employee_id) INTO 2 BUCKETS
必须使用INSERT方式加载数据
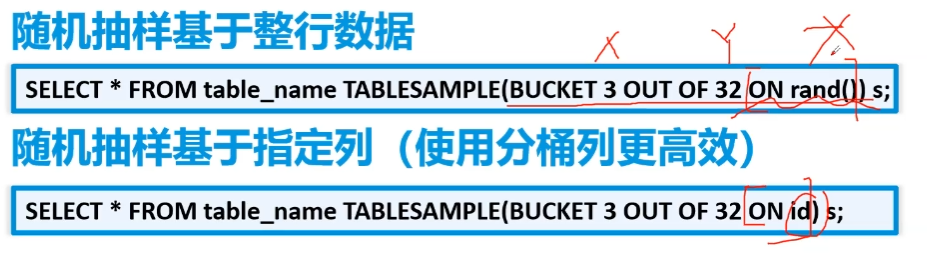
分桶抽样

第一句话,第一个3是从哪个桶开始抽取。32可大于可小于桶数,代表取
桶数/32个桶的数据rand()为随机采样,rand(num)为伪随机
除此之外,可以
1
2
3select * from mydemo.mybucket tablesample(40 percent) -- 百分比采样
select * from mydemo.mybucket tablesample(20B) -- 字节采样
select * from mydemo.mybucket tablesample(4 rows) -- 按行采样
B.例子1jp
开启分桶功能
1
set hive.enforce.bucketing=true
设置reduce个数和桶的数量一致
1
set mapreduce.job.reduces=4
创建1个分桶表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8create table mydemo.mybucket(
id int,
name string,
gender string,
age int
)
clustered by (id) into 4 buckets
stored as textfile插入数据
1
2insert into mydemo.mybucket values(1,'zs','男',20),(2,'ls','男',20),(3,'ww','男',20),(4,'zl','男',20),(5,'sq','男',20),(6,'wb','男',20),(7,'cq','男',20),
(8,'es','男',20),(9,'io','男',20),(10,'zw','男',20)结果
四个小文件,四个reduce,分区是多文件夹
第一个中
1
28es男20
4zl男20数据采样
拿了1、3桶的所有数据
1
select * from mydemo.mybucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2) s
拿1桶所有
1
select * from mydemo.mybucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 4) s
拿半个桶的
1
select * from mydemo.mybucket tablesample(bucket 1 out of 8) s
11.分区和分桶的不同
- 分区是表的部分列的集合,可以为频繁使用的数据建立分区,这样查找分区中的数据时就不需要扫描全表,这对于提高查找效率很有帮助
- 不同于分区对列直接进行拆分,桶往往使用列的哈希值对数据打散,并分发到各个不同的桶中从而完成数据的分桶过程
- 分区和分桶最大的区别就是分桶随机分割数据库,分区是非随机分割数据库
- 分区在底层是一个个文件夹,分桶是一个个文件
12.Hive视图(View)
A.介绍
视图概述
- 通过隐藏子查询、连接和函数来简化查询的逻辑结构
- 只保存定义,不存储数据
- 如果删除或更改基础表,则查询视图将失败
- 视图是只读的,不能插入或装载数据
应用场景
- 将特定的列提供给用户,保护数据隐私
- 用于查询语句复杂的场景
Hive侧视图(Lateral View)

举例
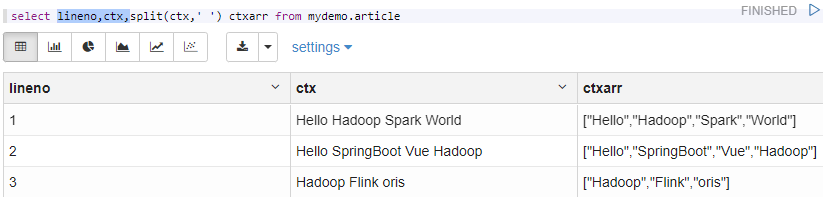
最早左边,分为右边,最后变成
1
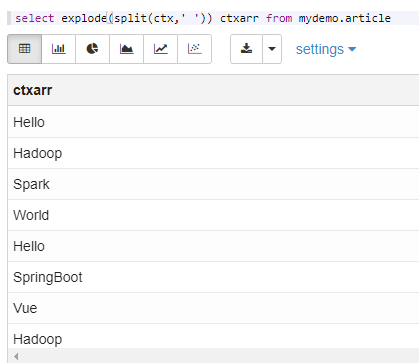
select lineno,ctx,split(ctx,' ') ctxarr from mydemo.article

这样子就最终

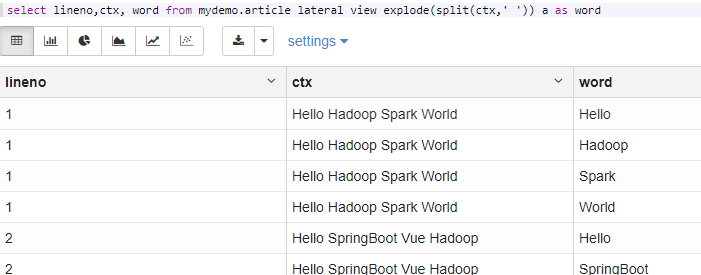
但是不知道是属于哪个,因此可以用视图
1
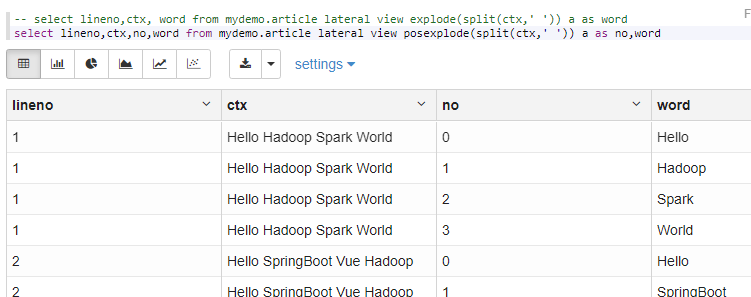
select lineno,ctx, word from mydemo.article lateral view explode(split(ctx,' ')) a as word

还可以带上排序
1
select lineno,ctx,no,word from mydemo.article lateral view posexplode(split(ctx,' ')) a as no,word

==explode炸开==比较重要,一列值分割转行。和真正的列转行有区别,真正的列转行是多列转行,用的是多次查询后Union
13.Hive高级查询
A.查询
基本和mysql相同,有个rlike
rlike后面跟正则,形如
select * from mydemo.mybucket where name rlike 'z[a-z]*'CTE语法
with t1 as
join方式
B.
c.
14.一次练习
- 上课商店销售分析练习
A.商店销售分析练习1-DOS
在hadoop上建立存储数据的文件夹 并上传文件到对应的文件夹
1
2
3
4
5
6
7%sh
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /storeanaly/customer
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /storeanaly/store
hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /storeanaly/tran
hdfs dfs -put /opt/testdata/jydata/customer_details.csv /storeanaly/customer
hdfs dfs -put /opt/testdata/jydata/store_details.csv /storeanaly/store
hdfs dfs -put /opt/testdata/jydata/transaction_details.csv /storeanaly/tran创建映射原始文件的数据仓库ODS_SALE
1
create database ods_sale
在近源层数据库中创建映射的数据表-ods_customer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21%hive
create external table ods_sale.ods_customer(
customer_id string,
first_name string,
last_name string,
email string,
gender string,
address string,
country string,
language string,
job string,
credit_type string
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
with serdeproperties(
"separatorChar"=",",
"quoteChar"="\"",
"escapeChar"="\\"
)
location '/storeanaly/customer'
tblproperties("skip.header.line.count"="1")在近源层数据库中创建映射的数据表-ods_store
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14%hive
create external table ods_sale.ods_store(
store_id string,
store_name string,
employee_number string
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
with serdeproperties(
"separatorChar"=",",
"quoteChar"="\"",
"escapeChar"="\\"
)
location '/storeanaly/store'
tblproperties("skip.header.line.count"="1")在近源层数据库中创建映射的数据表-ods_trans
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18%hive
create external table ods_sale.ods_trans(
transaction_id string,
customer_id string,
store_id string,
price string,
product string,
trandate string,
trantime string
)
row format serde 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
with serdeproperties(
"separatorChar"=",",
"quoteChar"="\"",
"escapeChar"="\\"
)
location '/storeanaly/tran'
tblproperties("skip.header.line.count"="1")对ods_customer进行数据探索工作
每一个表的逐条数据进行探索,格式对不对,有没有重复等等,并且要有一定的处理方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28%hive
-- select count(1) from ods_sale.ods_customer -- 500
-- select count(customer_id) from ods_sale.ods_customer where trim(customer_id)!=""
-- select count(distinct customer_id) from ods_sale.ods_customer
-- select count(1) from ods_sale.ods_customer where customer_id rlike '^[0-9]+$'
-- select count(*) from ods_sale.ods_customer where first_name is null or last_name is null or trim(first_name)='' or trim(last_name)=''
-- select concat(first_name,last_name) from ods_sale.ods_customer group by concat(first_name,last_name) having count(concat(first_name,last_name))>1
-- select * from ods_sale.ods_customer where email is not null and trim(email)!='' and email not rlike '^([0-9a-zA-Z]+@[0-9a-zA-Z]+(\\-[0-9a-zA-Z]+)?(\\.[0-9a-zA-Z]+)?\\.[0-9a-zA-Z]+)$' -- 邮箱域名地址中可能存放在 - 字符 或者只有1个字符的情况
-- select gender from ods_sale.ods_customer group by gender
-- with t1 as(select country,count(1) from ods_sale.ods_customer group by country)
-- select * from t1 where country=''
---探索ods_store
-- select * from ods_sale.ods_store
-- 探索ods_sale.ods_trans
-- select count(*) from ods_sale.ods_trans -- 8100
-- select count(transaction_id) from ods_sale.ods_trans where trim(transaction_id)!=""
-- select count(distinct transaction_id) from ods_sale.ods_trans -- 8000 有100行是重复的 修改订单编号 8004 8004_1
-- select transaction_id from ods_sale.ods_trans group by transaction_id having count(transaction_id)>1
-- with t1 as(select distinct * from ods_sale.ods_trans) select count(1) from t1
-- select count(t.customer_id) from ods_sale.ods_trans t inner join ods_sale.ods_customer c on t.customer_id=c.customer_id
-- select store_id from ods_sale.ods_trans group by store_id
-- select * from ods_sale.ods_trans where price not rlike '^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]{1,})?$'
-- select * from ods_sale.ods_trans where trim(product)=''
-- select * from ods_sale.ods_trans where trandate not rlike '^[1,2][0-9]{3}\-[0-9]{1,2}\-[0-9]{1,2}$'
-- select * from ods_sale.ods_trans where trantime not rlike '^[0-9]{1,2}:[0-9]{1,2}$' -- 10:32 PM将此种数据转为24小时制 22:32
B.商店销售分析练习2-DWD
创建数据明细层数据库dwd_sale
1
create database dwd_sale
根据ods的customer表导入dwd的customer
这步其实是可以压缩的
1
create table dwd_sale.dwd_customer as select * from ods_sale.ods_customer
根据ods的store表导入dwd的store
1
create table dwd_sale.dwd_store as select * from ods_sale.ods_store
5 创建自定义事件处理函数
跳到15那的Java示例1
上传jar包到hdfs
1
2hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /func
hdfs dfs -put /opt/timefunc-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar /func在hive上使用hdfs上的jar包创建永久函数
1
create function timehandler as 'com.njupt.timefunc.TimeChange' using jar 'hdfs://192.168.179.139:9000/func/timefunc-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar'
如果jar包错了,要在idea中清理缓存File-invalidate caches
然后再hive中要先drop function,再重启zeppelin和hive
最后再来一遍
创建自定义事件处理函数
1
2
3
4
5
6-- create table dwd_sale.dwd_trans like ods_sale.ods_trans -- 执行一次
with
t2 as(select t.*,row_number() over(partition by transaction_id order by customer_id) rank from ods_sale.ods_trans t),
t3 as(select case when rank=1 then transaction_id else concat(transaction_id,'_',rank) end transaction_id,
customer_id,store_id,price,product,trandate,timehandler(trantime) as trantime from t2)
insert into dwd_sale.dwd_trans select * from t3
C.商店销售分析练习3-DWS
- 数据服务层,用于业务处理
- 这边没有什么要用的,直接导进来就好了
创建dws数据服务层数据
1
create database dws_sale
将dwd中的表导入到dws层 构建数据模型 并做初步聚合工作
1
2
3create table dws_sale.dws_customer as select * from dwd_sale.dwd_customer
create table dws_sale.dws_store as select * from dwd_sale.dwd_store
create table dws_sale.dws_trans as select * from dwd_sale.dwd_trans
D.商店销售分析练习3-ADS
创建数据应用层数据库ADS
1
create database ads_sale
销售主题域-指标1 查询各国顾客表占比
1
2
3
4
5with
t1 as(select count(1) cnt_cust_number from dws_sale.dws_customer),
t2 as(select country,count(1) country_cust_number from dws_sale.dws_customer group by country),
t3 as(select t2.*,t1.cnt_cust_number from t1 cross join t2)
select country,(country_cust_number*1.0/cnt_cust_number)*100 kindCountryPerc from t3销售主题域-指标2 查询订单表中共有多少不同顾客下过订单和多少顾客没有下过订单
1
2
3
4
5
6
7with
t1 as(select customer_id from dws_sale.dws_trans group by customer_id),
t2 as(select c.customer_id,t.customer_id cid from dws_sale.dws_customer c left join t1 t on c.customer_id=t.customer_id),
t3 as(select customer_id from t2 where cid is null)
select 'gooduser' cust, count(1) number from t1
union all
select 'baduser' cust,count(1) number from t3销售主题域-指标3 查询商品表中购买数量前五的商品
1
2
3
4with
t1 as(select product,count(1) buy_num from dws_sale.dws_trans group by product),
t2 as(select product,buy_num,rank() over(order by buy_num desc) rk from t1)
select * from t2 where rk <=5
15.Hive函数和Java

- UDF相当于出一个 UDAF UDTF
- UDF一进一出
- UDAF:多进一出,类似max,min
- UDTF:一进多出,类似explode
A.UDF
总体
User Defined Function

Java示例1
导入包
比较难导入
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId>
<artifactId>hive-exec</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>时间变化pm am 或者没有改成24小时
要多考虑边界
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46package com.njupt.timefunc;
import org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.UDF;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class TimeChange extends UDF {
/**
*
* @param time 3:41 3:41 AM 3:41 PM
* @return
*/
public String evaluate(String time){
int hour = Integer.parseInt(time.split(":")[0]);
if (hour >= 12) {
Pattern tm = Pattern.compile("([0-9]{1,2}:[0-9]{1,2}).*");
Matcher mt = tm.matcher(time);
mt.find();
return mt.group(1);
} else {
Pattern amReg=Pattern.compile("(.*)[aA][mM]");
Pattern pmReg=Pattern.compile("(.*)[pP][mM]");
Matcher amM = amReg.matcher(time);
Matcher pmM = pmReg.matcher(time);
if (amM.find()) {
// 上午时间
return amM.group(1).trim();
} else if (pmM.find()) {
// 下午时间
String pm = pmM.group(1).trim();
String[] times = pm.split(":");
return (Integer.parseInt(times[0])+12)+":"+times[1];
} else {
return time;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String t = "13:31 pM";
TimeChange tc = new TimeChange();
System.out.println(tc.evaluate(t));
}
}不要main,打包,放到hdfs所在机器上
跳到15那的Java示例1
上传jar包到hdfs
1
2hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /func
hdfs dfs -put /opt/timefunc-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar /func在hive上使用hdfs上的jar包创建永久函数
1
create function timehandler as 'com.njupt.timefunc.TimeChange' using jar 'hdfs://192.168.179.139:9000/func/timefunc-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar'
B.时间函数
1 | 除了mysql那些 |
C.字符串
1 | cast(xxx as int) -- 字符串转换 |
1 | select regexp_extract('zs 1999-12-15 football,pingpang','[a-z]+ ([0-9]{4}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{2}) .*',1) -- 出1999-12-15 |
D.类型转换函数和数学函数
E.日期函数
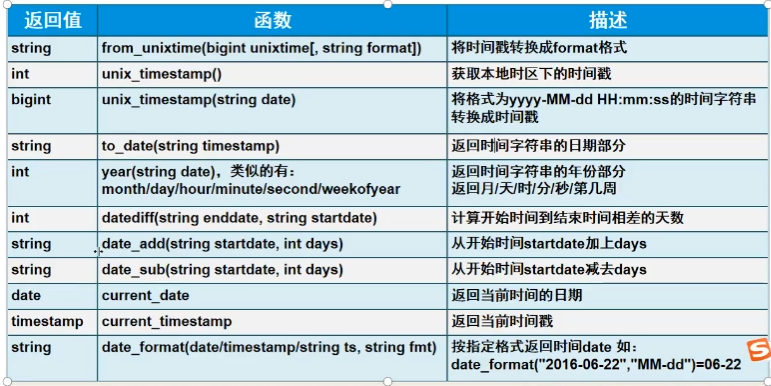
季度quarter
G.条件函数
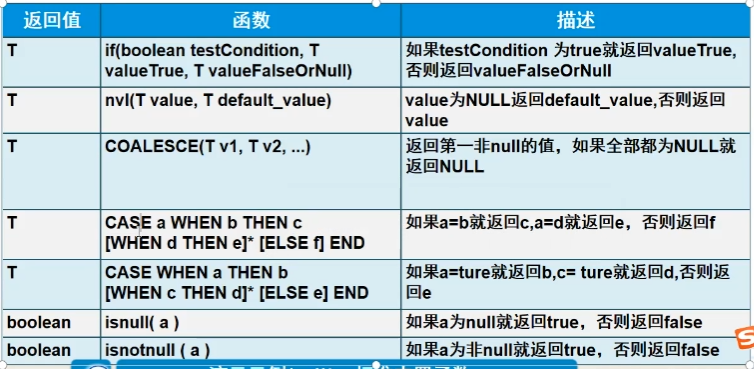
H.聚合函数

1 | select json_tuple('{"name":"zs","age":40}','name',"age") -- json中一定要"",但hive都可以,取出这两个值 |
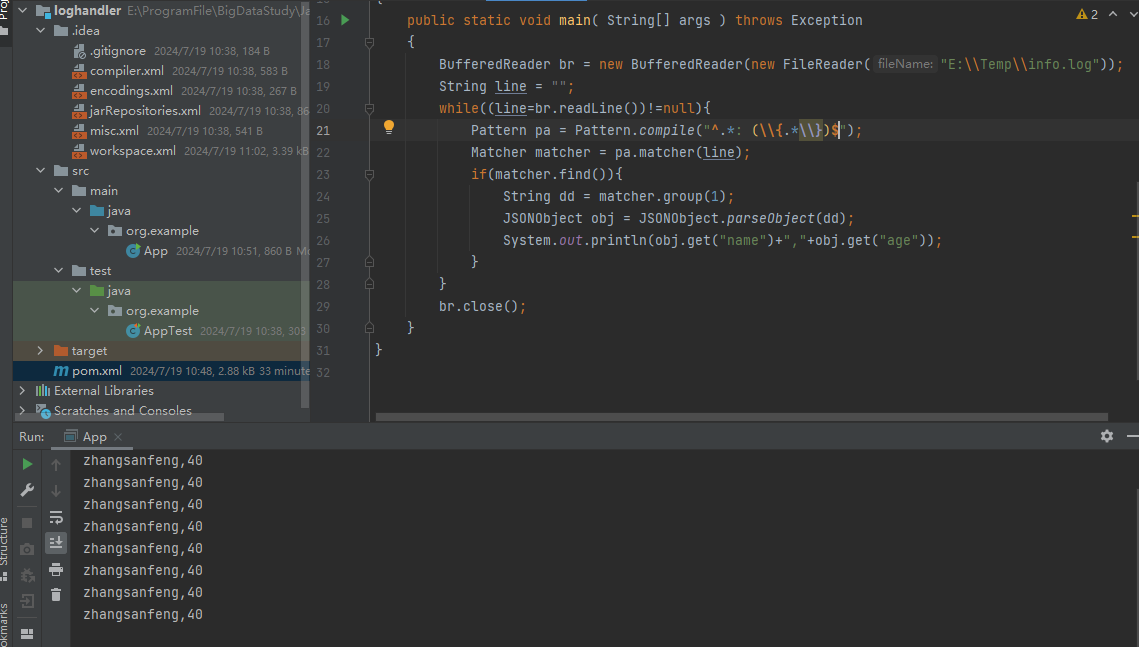
一个小例子
log文件形如
1
22024-07-19 10:30:19.313 INFO 21384 --- [http-nio-9090-exec-5] com.njupt.mydata.controller.DataCtrl : {"name":"zhangsanfeng","age":40}
2024-07-19 10:30:19.500 INFO 21384 --- [http-nio-9090-exec-6] com.njupt.mydata.controller.DataCtrl : {"name":"zhangsanfeng","age":40}hive读取
1
2
3
4
5
6create database md
create external table md.exp1(
data string
)
load data local inpath '/opt/testdata/info.log' into table md.exp1
select json_tuple(regexp_extract(data,'^.* : (\\{.*\\})$',1),'name','age') from md.exp1 where data rlike '^.* : \\{.*\\}$'结果

也可以用Java

I.数组操作
array_contains(array,str)str是否在array中- 制作数组
array('str1','str2')
16.MapJoin

17.排序
分类
全局排序(Order by)
每个MapReduce内部排序(Sort by)
分区排序(Distribute by)
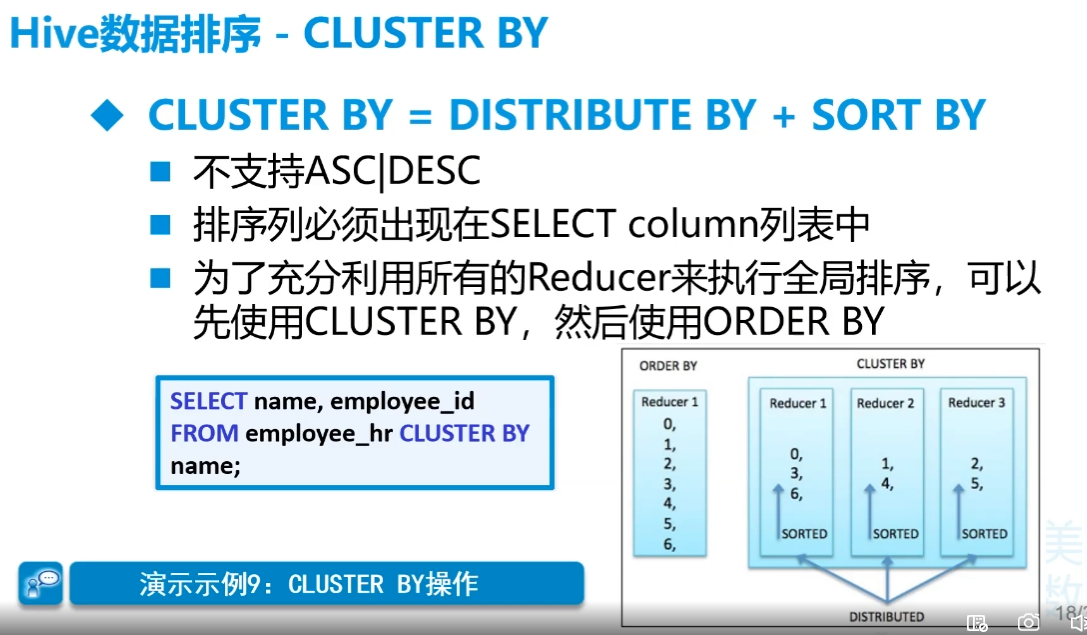
先分桶再排序(Cluster by)
Order by

不管怎么设置,order by最后一定只有一个reducer
Sort by和Distribute by

sort by是组内排序,因此要配合distribute by使用
distribute by相当于分区操作,默认使用hash
记得要提前设置reduce数量,否则默认为1,
set mapreduce.job.reduces=3设置个数cluster by
基本不用,局限太大。只能升序,而且分组和排序的字段只能同一个

18.自定义mapReduce数量
A.mapper
set mapred.max.split.size=204800设置分块大小,可以决定mapper数量,默认128M,单位为B
B.reducer
set mapreduce.job.reduces=3设置个数
19.单元格分组聚合
相当于mysql中的group_concat。collect_set,collect_list

从列直接聚合成一行,set是无序不可重复的,list是有序可重复
20.Hive事务
有,但不太用,因为主要是select操作,默认是不开的
原子性(atomicity,或称不可分割性)、一致性(consistency)、隔离性(isolation,又称独立性)、持久性(durability)。
21.Hive性能调优
explain 语句查看运行的过程- 文件格式
- textfile 天生横向扫描
- SequenceFile 把数据转为键值对,行格式,压缩比低,能直接看到切片效果,基本不用
- ORCFILE
stored as orc压缩比高,行列存储,每个块都有索引,自带zlib和znappy压缩器,加载时性能消耗大 - parquet,列式存储,存储嵌套式的数据
22.Hive数据倾斜
本地
23.Java连接Hive
- 不统计是不走mapReduce的
- 最后ADS中的内容就是要被调用而不被调用的
jdbc
加入的包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId>
<artifactId>hive-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>连接访问
jdbc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13public static void main( String[] args ) throws Exception
{
Class.forName("org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver");
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:hive2://192.168.179.139:10000/dws_supermark","root","root"); // hive的用户名和密码
PreparedStatement pstat = connection.prepareStatement("select credit_type,count(1) num from dws_supermark.dws_customs group by credit_type order by num desc limit 5");
ResultSet rs = pstat.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getString("credit_type")+" "+rs.getInt("num"));
}
rs.close();
pstat.close();
connection.close();
}
springboot
导入包
前面选sql中的mybatis的驱动,再后面自己加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hive</groupId>
<artifactId>hive-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency> 这是个连接池
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.19</version>
</dependency>配置application.yml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:hive2://192.168.179.139:10000/ads_supermark_user
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
initial-size: 5
min-idle: 5
max-active: 10
max-wait: 30000
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
test-while-idle: true
validation-query: select 1
mybatis:
config-location: classpath:mybatis.cfg.xml
mapper-locations: classpath*:mapper/*.xml
server:
port: 9090其他如后端框架mysql的连接
(七).离线数仓四层结构
自己总结的
- 例子在上面14的一次练习中有
近源层
单纯映射表,ODS,Operational Data Store
进行数据的探索
数据明细层
DWD,Data Warehouse Detail,进行数据清理
数据服务层
DWS,Data Warehouse Summary
维度表:名词表,如用户、商品。
看一个事实的维度,用户表是交易表的维度表。
事实表:动作表,如交易订单
可以进行一些数据的统计,做聚合等等
模型
星型模型,一个动作为中心,多维度查看。
雪花模型,从某个维度看维度再向事实
星座模型,多个维度看多个事实
数据应用层
ADS,Application Data Store
把要查询的内容查完之后存在表中,做指标,后续外部调用就不要使用MapReduce了。
最后结果甚至可以存放在Mysql中,因为最后统计的数据量并不是很大,如果要做二次统计就放Mysql
DWT层
如果是做指标的话,ADS层会换成DWT层
上面每一层都要有一个数据库
合起来称为数据仓库
后来讲的
(八)多次练习
1.某宝用户行为分析练习
创建数据仓库
create database taobao创建数据表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8create table taobao.userbehavior(
cust_id string,
sku_id string,
spu_id string,
useract string,
ts string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','导入数据
1
load data local inpath '/opt/testdata/UserBehavior.csv' into table taobao.userbehavior
数据探索
select * from taobao.userbehavior where cust_id not rlike '^[0-9]+$'数据清理(分区表按日分,将时间戳改为YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS)
建立分区表,用orc的方式存储
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10create table taobao.behaviorpart(
cust_id string,
sku_id string,
spu_id string,
useract string,
actiondate string
)
partitioned by (ymd string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
stored as orc动态分区塞入数据
1
2
3
4-- set hive.exec.dynamic.partition=true
-- set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict
-- insert into taobao.behaviorpart partition(ymd)
-- select t.*,date_format(actiondate,'yyyyMMdd') ymd from (select ub.cust_id,ub.sku_id,ub.spu_id,ub.useract,from_unixtime(cast(ub.ts as int)) actiondate from taobao.userbehavior ub) t但是由于硬盘的原因受到限制,因此用静态分区,逐分区塞入数据
静态分区塞入数据,中间步骤用临时表缓解硬盘压力,删掉前面的表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10-- alter table taobao.behaviorpart add partition(ymd='20171125') partition(ymd='20171126')
-- partition(ymd='20171127') partition(ymd='20171128') partition(ymd='20171129')
-- partition(ymd='20171130') partition(ymd='20171201') partition(ymd='20171202') partition(ymd='20171203')
-- create table taobao.tmp1 like taobao.userbehavior
-- insert into taobao.tmp1 select ub.cust_id,ub.sku_id,ub.spu_id,ub.useract,from_unixtime(cast(ub.ts as int)) actiondate from taobao.userbehavior ub
-- drop table taobao.userbehavior
insert into taobao.behaviorpart partition(ymd='20171202') select cust_id,sku_id,spu_id,useract,ts actiondate
from taobao.tmp1 where date_format(ts,'yyyyMMdd')='20171202' -- 一天天的导入
成交率
1
2
3
4
5-- 成交率
with
t1 as(select count(distinct cust_id) total_num from taobao.behaviorpart),
t2 as(select count(distinct cust_id) buy_num from taobao.behaviorpart where useract='buy')
select '成交率' say,t2.buy_num/t1.total_num closerate from t1 cross join t2复购率
1
2
3
4
5
6
7-- 复购率
with
t1 as(select count(distinct cust_id) buy_num from taobao.behaviorpart where useract='buy'),
t2 as(select cust_id from taobao.behaviorpart where useract='buy'),
t3 as(select cust_id from t2 group by cust_id having count(1)>1),
t4 as(select count(cust_id) s from t3)
select '复购率' say,t4.s/t1.buy_num closerate from t1 cross join t4转化漏斗(点击-收藏/加购-购买的数量关系)
1
2select count(if(useract='pv',1,null)) pv,count(if(useract='fav',1,null)) fav,
count(if(useract='cart',1,null)) cart,count(if(useract='buy',1,null)) buy from taobao.behaviorpart跳失率(点击单页面即退出的用户/全部点击用户数)
1
2
3
4with
t1 as(select count(1) dump_num from (select cust_id from taobao.behaviorpart where useract='pv' group by cust_id having count(cust_id)=1) t),
t2 as(select count(distinct cust_id) pv_total from taobao.behaviorpart where useract='pv')
select '跳失率' say,t1.dump_num/t2.pv_total lossrate from t1 cross join t2最活跃的用户Top10
1
select cust_id,count(1) active from taobao.behaviorpart group by cust_id order by active desc limit 10
最热门的商品Top10(浏览率最高的10个商品)
1
select sku_id,count(1) pv_num from taobao.behaviorpart where useract='pv' group by sku_id order by pv_num desc limit 10
统计每天的用户量、点击量、收藏量、加购量、购买量
1
select date_format(actiondate,'yyyy-MM-dd') addate,count(distinct cust_id) cnt_user,count(if(useract='pv',1,null)) cnt_pv,count(if(useract='fav',1,null))cnt_fav,count(if(useract='cart',1,null)) cnt_cart,count(if(useract='buy',1,null)) cnt_buy from taobao.behaviorpart group by date_format(actiondate,'yyyy-MM-dd')
2.较为真实的用户行为分析
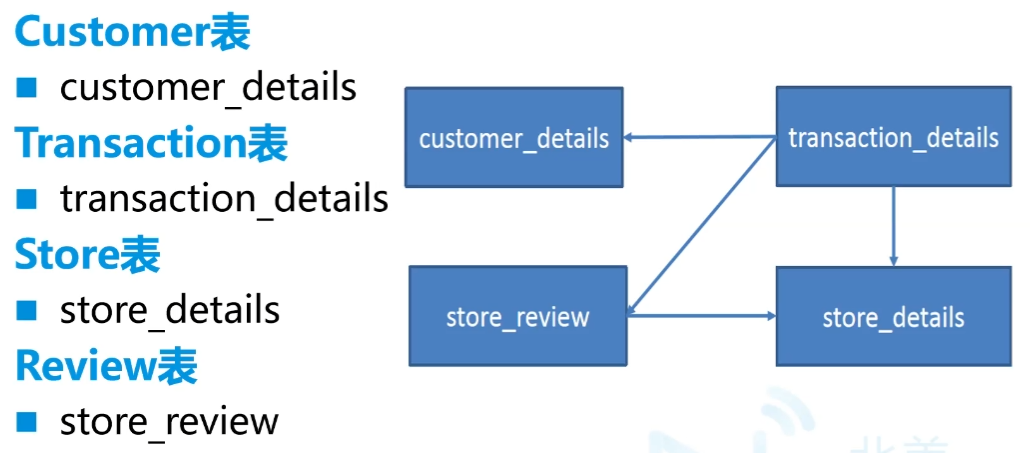
要求:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60customer_details.csv
customer_id,first_name,last_name,email,gender,address,country,language,job,credit_type,credit_no
store_details.csv
store_id,store_name,employee_number
store_review.csv
transaction_id,store_id,review_score
transaction_details.csv
transaction_id,customer_id,store_id,price,product,date,time
Customer分析
6.1找出顾客最常用的信用卡
6.2找出客户资料中排名前五的职位名称
6.3在美国女性最常用的信用卡
6.4按性别和国家进行客户统计
Transaction分析-1
7.1计算每月总收入
7.2计算每个季度的总收入
7.3按年计算总收入
7.4按工作日计算总收入
7.5按时间段计算总收入(需要清理数据)
7.6按时间段计算平均消费
7.7按工作日计算平均消费
7.8计算年、月、日的交易总数
7.9找出交易量最大的10个客户
7.10找出消费最多的前10位顾客
Transaction分析-2
7.11统计该期间交易数量最少的用户
7.12计算每个季度的独立客户总数
7.13计算每周的独立客户总数
7.14计算整个活动客户平均花费的最大值
7.15统计每月花费最多的客户
7.16统计每月访问次数最多的客户
7.17按总价找出最受欢迎的5种产品
7.18根据购买频率找出最畅销的5种产品
7.19根据客户数量找出最受欢迎的5种产品
7.20验证前5个details
Store分析
8.1按客流量找出最受欢迎的商店
8.2根据顾客消费价格找出最受欢迎的商店
8.3根据顾客交易情况找出最受欢迎的商店
8.4根据商店和唯一的顾客id获取最受欢迎的产品
8.5获取每个商店的员工与顾客比
8.6按年和月计算每家店的收入
8.7按店铺制作总收益饼图
8.8找出每个商店最繁忙的时间段
8.9找出每家店的忠实顾客
8.10根据每位员工的最高收入找出明星商店
Review分析
9.1在ext store review中找出存在冲突的交易映射关系
9.2了解客户评价的覆盖率
9.3根据评分了解客户的分布情况
9.4根据交易了解客户的分布情况
9.5客户给出的最佳评价是否总是同一家门店
八.HBase
(一)前期
- 争议较大
- NoSQL
- 目的是存储海量数据,在不启用MapReduce的情况下,快速查数据,列式存储
- 实时流的存储往往用HBase,是Hadoop原生的。Doris的好处是用sql,但存储能力和HBase差不多
- 鼓励冗余

- 比较昂贵,虽然效率高,但是用得人少
- 面试重点:
- Hbase行键是如何设计的
- 优化:预处理分析
- 热点问题
- 随机读写
- 百亿数据必用,十亿左右可用可不用,适合PB级别的数据
- hbase版本和hadoop有要求
(二)内容
1.特点
- 数据访问速度快,响应时间约2-20毫秒
- 支持随机读写,每个节点20k~100k+ops/s
- 可扩展性,可扩展到20,000+节点
- 高并发
2.应用场景
- 增量数据-时间序列数据
- 高容量,高速写入
- HBase之上有OpenTSDB模块,可以满足时序类场景
比如传感器,系统监控,股票行情监控等
- 内容服务-Web后端应用
- Facebook和Alibaba
- 费用比较高
3.随机存取

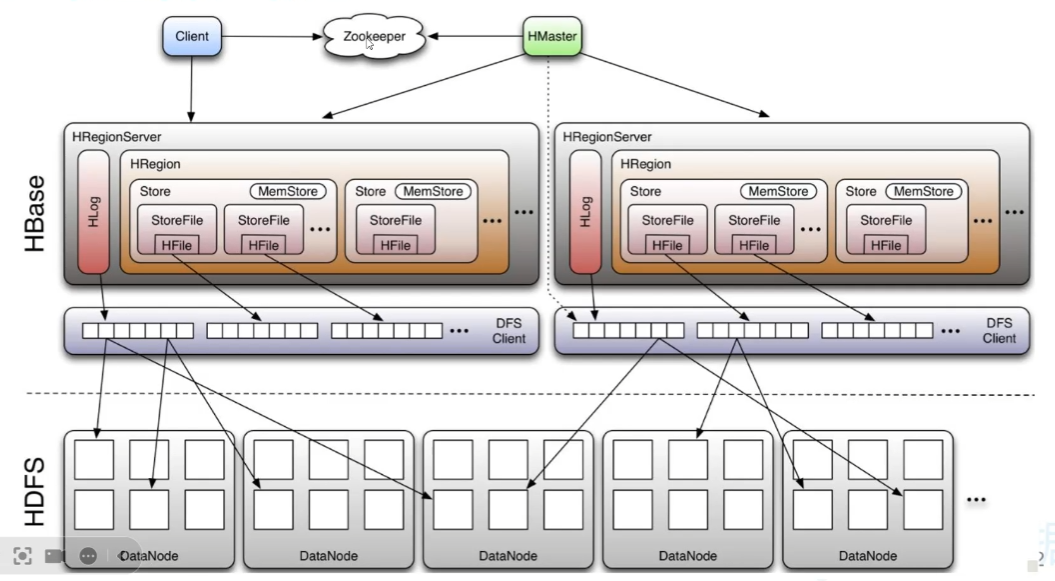
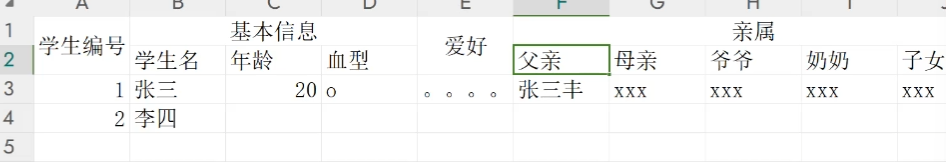
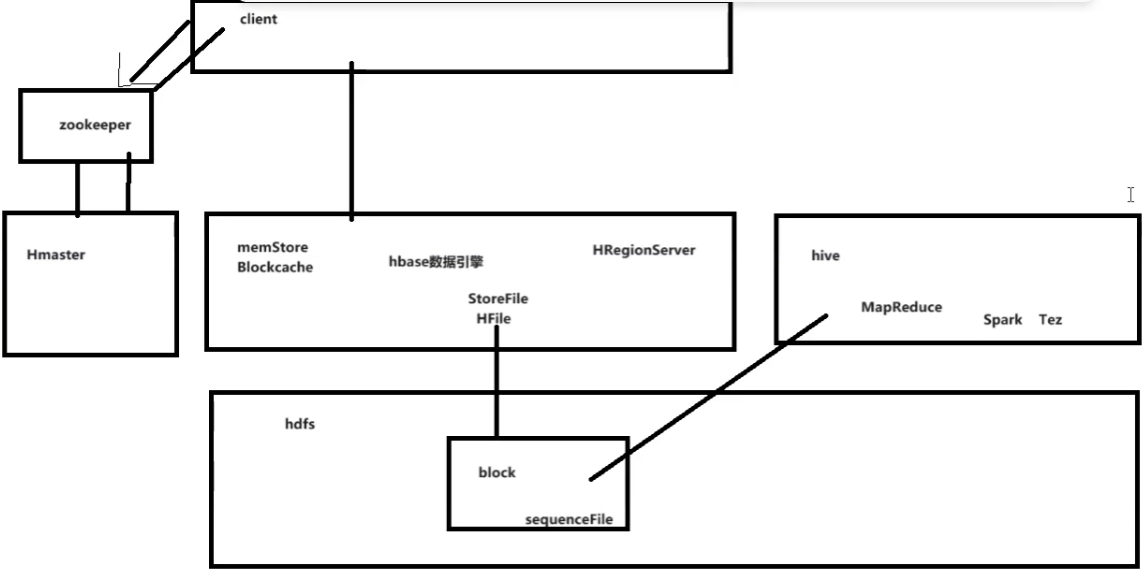
列存储,列簇,就是多个列为一个列簇。如下图所示,基本信息、亲属就是列簇。

然后把每个列簇分出来,分成类似于多张表,但是这张表我们称为列簇,我们看上去仍然是一张表。中间的关联是用的行键(而不是主外键)。一个store就是一个列簇,一般最多两三个列簇
实际上的架构每行都为
行键 列簇 时间戳 列名 值冗余性很高,但是通过稀疏索引可快速找到相应列,实现随机存取
物理架构

StoreFile相当于是hdp中的block,对应一张表的一个列簇,一个Store相当于一张表,
行太多时,就分Region,多Region上下相连,才是完整的表
列太多时,分割成列簇,就是一个个StoreFile
MemStore是写入的缓冲区,达到容量条件或者时间要求会写入HDFS形成HFile
HLog(WAL)日志文件,因为MemStore在内存中,因此可能会导致丢失,先写入WAL,再放内存就可以还原了
HRegion分割是按hash,Store内部是按字典排序
(三)单机安装
前提要有Hadoop
先安装zookeeper,zookeeper-3.4.5-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz放到
/opt1
2
3
4
5cd /opt
tar -zxf zookeeper-3.4.5-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz
mv zookeeper-3.4.5-cdh5.14.2 soft/zk345
cd soft/zk345/conf/
cp zoo_sample.cfg zoo.cfgvim zoo.cfg1
2dataDir=/opt/soft/zk345/data
server.1=192.168.179.139:2888:3888vim /etc/profile1
2
3#Zookeeper Env
export ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/opt/soft/zk345
export PATH=$PATH:$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin1
2
3source /etc/profile
# 在hadoop启动的情况下
zkServer.sh start多个QuorumPeerMain
hbase安装,把hbase-1.2.0-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz放到
/opt下1
2
3
4cd /opt
tar -zxf hbase-1.2.0-cdh5.14.2.tar.gz
mv hbase-1.2.0-cdh5.14.2 soft/hbase120
cd soft/hbase120/confvim hbase-env.sh1
2export JAVA_HOME=/opt/soft/jdk180
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false # 用外部的zookeepervim hbase-site.xml1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13<property>
<name>hbase.rootdir</name>
<value>hdfs://192.168.179.139:9000/hbase</value>
</property>
<!—单机模式不需要配置,分布式配置此项为true,单机好像也得true-->
<property>
<name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.property.dataDir</name>
<value>/opt/soft/zk345/hbase</value>
</property>vim /etc/profile
1
2
3#Hbase Env
export HBASE_HOME=/opt/soft/hbase120
export PATH=$PATH:$HBASE_HOME/bin1
2
3
4
5
6source /etc/profile
start-hbase.sh
# 多出HRegionServer HMaseter
# 进入
hbase shell
stop-hbase.sh
(四)使用
1.第一次使用
1 | zkServer.sh start |
删除过程要按住ctrl删除,否则会往后删
2.各种命令
命令集

名空间(namespace)-对应数据库
1
create_namespace '名字'
建表
1
create '名空间:表名','列簇1','列簇2'...
插入数据
一次只能插入一格
1
put '名空间:表名',行键,'列簇名:列名','字符串数据'或者数字
查看数据
1
scan '名空间:表名'
- 结果 能看到有插入的时间戳

查单个
1
get '名空间:表名',行键
查前5行
1
scan '名空间:表名',{LIMIT=>5}
修改 和插入一样,会直接覆盖
1
put '名空间:表名',行键,'列簇名:列名','字符串数据'或者数字
删除数据
删一格
1
delete '名空间:表名',行键,'列簇名:列名'
删一行
1
delete '名空间:表名',行键
删全部数据
1
truncate '名空间:表名'
删表
1
2
3先关停表再删除
disable '名空间:表名'
drop '名空间:表名'
统计数
每1000行统计一次,太慢
1
count '名空间:表名'
外部统计
1
hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.RowCounter '库:表' ['outputfile']
3.外部导入数据
- csv文件不要表头
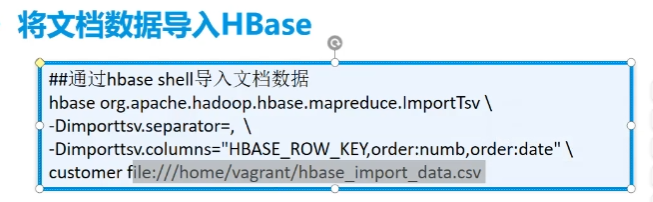
1 | hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.ImportTsv \ |
4.第一次hive操作hbase
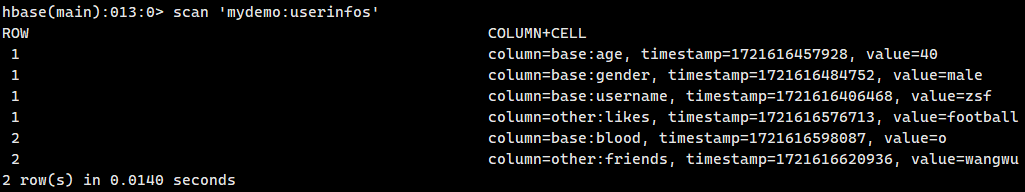
首先hbase中有一个表mydemo:userinfos,两个列簇:base和others
数据三列都在base中,分别为name,age,gender
并不是很好,只是对hbase做了映射,还是得走mapreduce而不会用hbase。因为hive直接读取了hbase在hdfs上的文件
hbase是用SequenceFile 的方式存储的

因此这个方式做离线数仓还行,用Java直接对client下命令比较好
用hive映射操作hbase表(insert select)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14create database exp;
create external table exp.cutoms(
id string,
username string,
age int,
sex string
)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (
"hbase.columns.mapping" = ":key,base:name,base:age,base:gender"
)
TBLPROPERTIES (
"hbase.table.name" = "mydemo:userinfos"
);
5.Java控制hbase
- 走的是hbase的底层,速度比hive快得多
- 项目名hivejdbc
导入依赖
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0</version>
</dependency>使用
==
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts加虚拟机的ip 主机名,否则读不到表==读数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35package org.example;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class App1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
// 设置zookeeper地址
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "192.168.179.139:2181");
// 开启hbase数据库连接
Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
System.out.println("连接开启"+connection);
// 读取数据
// 找到你要操作的表
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("mydemo:userinfos"));
System.out.println("找到表:"+table);
// 拿数据
Scan scan = new Scan();
ResultScanner rss = table.getScanner(scan);
System.out.println("获得数据集合:"+rss);
for (Result rs : rss) {
System.out.println(
new String(rs.getRow())+ " "+
new String(rs.getValue("base".getBytes(),"name".getBytes()))+" "+
new String(rs.getValue("base".getBytes(),"age".getBytes()))+" "+
new String(rs.getValue("base".getBytes(),"gender".getBytes())));
}
connection.close();
}
}写数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44package org.example;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class App1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
// 设置zookeeper地址
config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "192.168.179.139:2181");
// 开启hbase数据库连接
Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
System.out.println("连接开启"+connection);
// 读取数据
// 找到你要操作的表
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("mydemo:users"));
System.out.println("找到表:"+table);
// 添加一条数据
// Put put = new Put("1".getBytes());
// put.addColumn("base".getBytes(), "uname".getBytes(), "zs".getBytes());
// put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),"20".getBytes());
// put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"gender".getBytes(),"男".getBytes());
// table.put(put);
// 一次性添加1000条数据
Random rand = new Random();
List<Put> putss = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 2; i <= 1002; i++) {
Put put = new Put((""+i).getBytes());
put.addColumn("base".getBytes(), "uname".getBytes(), ("zs"+i).getBytes());
put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),(""+rand.nextInt(100)).getBytes());
put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"gender".getBytes(),(i%2==0?"男":"女").getBytes());
putss.add(put);
}
table.put(putss);
connection.close();
}
}
6.Java不定长度批量插入
包和前面一样
用缓存的方式
包用高版本的,才有定时刷缓冲区
1
2
3
4
5<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>package org.example; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName; import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*; import java.util.Random; public class App1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create(); // 设置zookeeper地址 config.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "192.168.179.139:2181"); // 开启hbase数据库连接 Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config); System.out.println("连接开启"+connection); // 读取数据 // 找到你要操作的表 Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf("mydemo:users")); System.out.println("找到表:"+table); // 一次性添加1000条数据 Random rand = new Random(); // 准备一个特定的缓存对象 BufferedMutatorParams bmp = new BufferedMutatorParams(TableName.valueOf("mydemo:users")); bmp.writeBufferSize(1024*1024); // 设置当数据满1kb时就填充数据到hdfs bmp.setWriteBufferPeriodicFlushTimerTickMs(2000); // 设置如果缓存区没有填满 此时刷新时间到达也会触发写操作 // bmp.setWriteBufferPeriodicFlushTimeoutMs(3000); 超时时间 BufferedMutator bm = connection.getBufferedMutator(bmp); for (int i = 1; i <= 34225; i++) { Put put = new Put((""+i).getBytes()); put.addColumn("base".getBytes(), "uname".getBytes(), ("zs"+i).getBytes()); put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),(""+rand.nextInt(100)).getBytes()); put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"gender".getBytes(),(i%2==0?"男":"女").getBytes()); put.addColumn("base".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),"51CTO博客已为您找到关于java 设置指定时间运行的相关内容,包含IT学习相关文档代码介绍、相关教程视频课程,以及java 设置指定时间运行问答内容。更多java 设置指定时间运行".getBytes()); bm.mutate(put); } // bm.flush(); bm.close(); connection.close(); } }create 'mydemo:uuu','base',{SPLITS=>['0|','1|','2|']}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
### (五)进阶学习
#### 1.Region管理
- Region拆分
- 当一个Region大到一定程度,会进行分裂(split)
- HBase可以通过Region Split达到负载均衡
- Region默认大小10G
- Region合并
- 如果删除了大量数据,很多Region变小,这时候分成多个Region就很浪费,可以把Region合并起来,Region的合并不是为了性能考虑,主要是出于维护的目的
- Region的拆分要重计算row_key,所以动态分不好,事先分区比较好。即为***预分区***
##### A.Region预分区
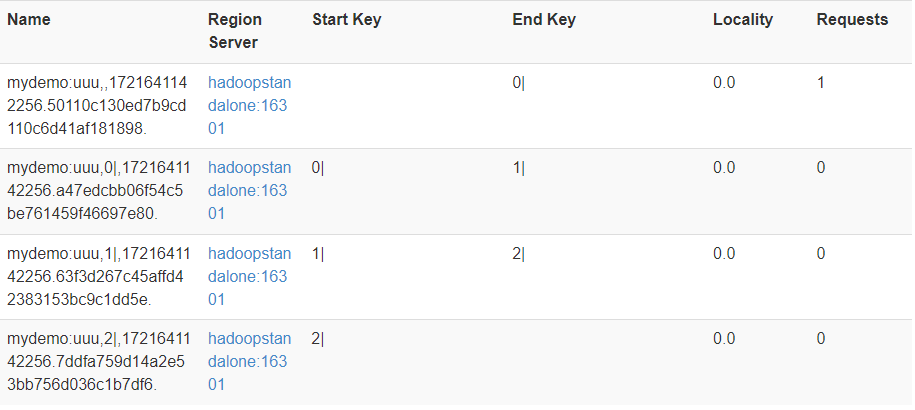
- 将数据分布在多Region上,防止自动分区,默认10G,每个表2、3列簇。要设计Row_key,**默认是按照Ascii来的**
- 创建预分区,三个数字四个区,|是124,因此比前面数字小于等于的都会在左边,并非是数字,而是字符put 'mydemo:uuu','012356bds','base:name','zs'1
2
3
- 插入一条数据结果:

B.预分区Row_key设计
- (防止数据热点)
最后
- 标题: 大数据学习笔记2-Hive、Hbase
- 作者: Sabthever
- 创建于 : 2025-02-17 10:39:34
- 更新于 : 2025-10-09 16:14:31
- 链接: https://sabthever.cn/2025/02/17/technology/bigdata/Hadoop2-Hive-Hbase/
- 版权声明: 本文章采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 进行许可。